Teaching Assistant – Digital Control Systems (SE 420/SE 511)
Graduate course, University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign, Industrial & Enterprise Systems Engineering, 2023
Course Description
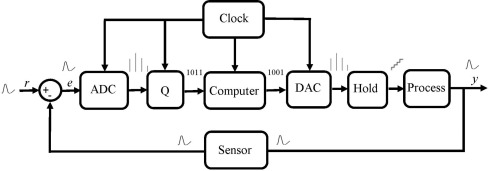
Digital Control Systems covers the theory, analysis, and design of discrete-time control systems implemented on digital computers. Topics include linear discrete-time models, sampling and reconstruction, Z-transform methods, digital filters, closed-loop stability, state-space representation, state estimation, pole placement, and implementation issues such as quantization and computational delay. Laboratory work and MATLAB/Simulink exercises reinforce real-world applications. This course is offered for 4 undergraduate or 4 graduate credit hours. Prerequisite: SE 320.
Teaching Assistant Role
I served as the primary teaching assistant for SE 420/511 during Fall 2023. My responsibilities included supporting students in modeling, analysis, and real-time implementation of digital control algorithms. I worked closely with the instructor to help students connect theoretical results with simulation and practical applications.
Responsibilities
- Held weekly office hours to assist students with discrete-time system modeling, stability analysis, and controller implementation.
- Guided students through MATLAB/Simulink labs involving:
- Z-transform analysis
- Discrete-time root locus
- Digital PID tuning
- Discretization of continuous-time controllers
- State feedback and observer design
- Supported students in homework assignments, exam preparation, and conceptual understanding of sampling, aliasing, pole placement, and state estimation.
- Assisted with grading of problem sets, exams, and design-focused assignments.
- Provided debugging help for numerical issues, discretization errors, and simulation instability.
- Offered supplemental examples demonstrating implementation challenges such as quantization, zero-order hold behavior, and computational delay.
Topics Covered
- Discrete-time system modeling and difference equations
- Z-transform and transfer functions for digital systems
- Sampling, reconstruction, and aliasing
- Digital filter design and implementation
- Closed-loop stability analysis (Jury test, root locus)
- State-space representation and discrete-time controllability/observability
- Design of state estimators and observers
- Discretization of continuous-time controllers (ZOH, Tustin, pole matching)
- Practical implementation limits in digital control systems